Introduction
This sample chapter extracted from the book, The Modern Cryptograhy CookBook . The Book theme isCryptography is for EveryOne. Learn from Crypto Principle to Applied Cryptography With Practical ExampleGet this book on Just $9 by availing coupon discount
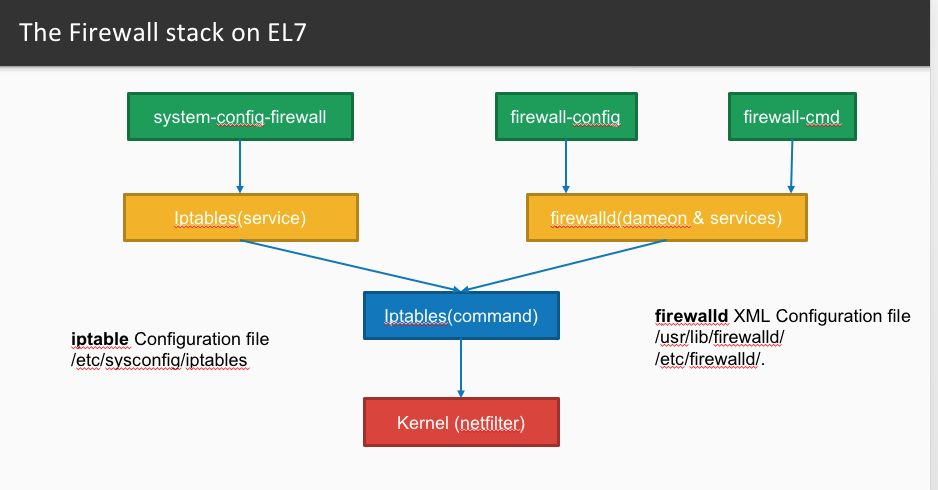
IPtables is the firewall service that is available in a lot of different Linux Distributions. While modifying it might seem difficult to dealt with at first, this writeup should be able to show you just how easy it is to use and how quickly you can be on your way mucking around with your firewall
iptables CHAINS
Iptables is made up of 5 tables, each associated to specific functionalities of the net filter and each split into several "chains", specifying the functionalities of each table further-
INPUT - Used to control the behavior of INCOMING connections.
-
FORWARD - Used to control the behavior of connections that aren't delivered locally but sent immediately out.
-
OUTPUT - Used to control the behavior of OUTGOING connections.
-
PREROUTING: This chain is used to make any routing related decisions before (PRE)
sending any packets. Here is an example, we are redirecting any traffic
that just reached the server on port 80 to the port 8080:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080 -
FORWARD: As the name suggests, The
FORWARDchain ofFILTERtable is used to forward the packets from a source to a destination. Here is an example ofFORWARDchain where anyTCPtraffic received on port 80 on interfaceeth0meant for the host192.168.0.4will be accepted and forwarded to192.168.0.4:
You should use nat's PREROUTING only to change the destination address of the packets and filters FORWARD only for filtering (dropping/accepting packets).iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -d 192.168.0.4 -j ACCEPT
iptables Actions
- ACCEPT: Allow the connection
- DROP: Drop the connection (as if no connection was ever made; Useful if you want the system to disappear on the network)
- REJECT: Dont allow the connection but send an error back.
iptables Default Policy
In every linux system, the chain is configured with default ACTION, in order to know what is the default policysudo iptables -L | grep policy
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
How to Change Default iptables Policy
sysadmins can change the default policy byiptables --policy <CHAIN> <ACTCION>for example
iptables --policy INPUT DROP
iptables --policy OUTPUT ACCEPT
iptables --policy FORWARD DROP
iptables main command options
Get familiar you self with iptables rulesiptables -h , this is great place to start, some tipsiptables -Awill add the rule at the endiptables -Iwill add the rule at the top by defaultiptables -Dwill delete a rule (specify a rule number or specify the whole rule you want to remove for this option to work)iptables -Cwill check for the existence of a ruleiptables -FDelete all rules in chain or all chains
Most common IPtables rules
-
iptables: How to Block All Traffics
iptables -F iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT iptables -A OUTPUT -j REJECT iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT -
iptables How to Block Incoming Traffic Only
iptables -F INPUT iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT -
iptables How Block Outgoing Traffic Only
iptables -F OUTPUT iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -j REJECT -
iptables: How to Block Specific Incoming port or Service
This will block http service any incoming traffic
oriptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j REJECT
to allow only local interfaces for httpiptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport www -j REJECT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j REJECT -
iptables: How to block specific host
This will block all access by that host
iptables -A INPUT -s <remote_ip> -j REJECT -
iptables: How to block outgoing to specific hosts
iptables -A INPUT -s <remote_ip> -j REJECT -
iptables: How to allow access to specific mac address only
iptables -A INPUT -m mac --mac-source <mac_address> -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT -
iptables: How to allow only SSH
iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport ssh -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT -
iptables: How to block all outgoing connection for example telnet
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport telnet -j REJECT -
iptables: How to block ping
oriptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP -
iptables: How to configure connection wait
Makes iptables wait 15 seconds between new connections from the same IP on port 22 (SSH):
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -i eth0 -m state --state NEW --dport 22 -m recent --update --seconds 15 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -i eth0 -m state --state NEW --dport 22 -m recent --set -j ACCEPT -
iptables: How to Block Smurf attacks
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type address-mask-request -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp -j DROP -
iptables: How to drop excessive RST packets to avoid smurf attacks
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags RST RST -m limit --limit 2/second --limit-burst 2 -j ACCEPT -
iptables: How to do Port Forwarding
This rules will forward all the incoming request on port 80 to port 8080
This rules will forward all the incoming request on port 80 from localhost to port 8080iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080
iptables -t nat -I OUTPUT -p tcp -d 127.0.0.1 --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080 -
iptables How to List IPtables Rules
iptables -L iptables -t nat --line-numbers -n -L -
iptables: How to save rule changes made to iptables
Ubuntu: sudo /sbin/iptables-save RedHat / Centos: /sbin/service iptables save Others: /etc/init.d/iptables save Generic: iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables -
How to restore iptables rules from file
sudo iptables-save | sudo tee /etc/iptables.conf
sudo iptables-restore < /etc/iptables.conf
-
How to flush clear all iptables rules
This command will not clear NAT rules
Note if there are NAT rule, then to flush itiptables -F
iptables -t nat -F -
iptables: How to delete PREROUTING NAT rule
First find out what line it is byiptables -t nat -L --line-numbers
Then delete the rule numberiptables -t nat -L --line-numbers Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination 1 REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:8082 redir ports 8083 2 REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:8084 redir ports 8083 Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination 1 REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere localhost tcp dpt:8084 redir ports 8083 2 REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere localhost tcp dpt:8082 redir ports 8083
iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING 2
-
iptables: How to do logging of iptbales
create a new rule chain that logs and drops in sequence:
Log All Dropped Outgoing Packets# Create a new chain called LOGGING iptables -N LOGGING #All the remaining incoming packets will jump to the LOGGING chain iptables -A INPUT -j LOGGING #Log the incoming packets to syslog (/var/log/messages) iptables -A LOGGING -m limit --limit 3/min -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables drop packets" --log-level 4 #Finally, drop all the packets that came to the LOGGING chain iptables -A LOGGING -j DROP
iptables -N LOGGING iptables -A OUTPUT -j LOGGING iptables -A LOGGING -m limit --limit 3/min -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables drop packets " --log-level 4 iptables -A LOGGING -j DROP -
iptables: How to build DDoS Rule in iptables
# Reject spoofed packets iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.0/8 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -s 169.254.0.0/16 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/12 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 127.0.0.0/8 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -s 224.0.0.0/4 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -s 240.0.0.0/5 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -d 240.0.0.0/5 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -s 0.0.0.0/8 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -d 239.255.255.0/24 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -d 255.255.255.255 -j DROP # Stop smurf attacks iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type address-mask-request -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type timestamp-request -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp -j DROP # Drop all invalid packets iptables -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state INVALID -j DROP iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP # Drop excessive RST packets to avoid smurf attacks iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags RST RST -m limit --limit 2/second --limit-burst 2 -j ACCEPT -
iptables How to block portscans
# Anyone who tried to portscan us is locked out for an entire day. iptables -A INPUT -m recent --name portscan --rcheck --seconds 86400 -j DROP iptables -A FORWARD -m recent --name portscan --rcheck --seconds 86400 -j DROP # Once the day has passed, remove them from the portscan list iptables -A INPUT -m recent --name portscan --remove iptables -A FORWARD -m recent --name portscan --remove # These rules add scanners to the portscan list, and log the attempt. iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 139 -m recent --name portscan --set -j LOG --log-prefix "Portscan:" iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 139 -m recent --name portscan --set -j DROP iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -m tcp --dport 139 -m recent --name portscan --set -j LOG --log-prefix "Portscan:" iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -m tcp --dport 139 -m recent --name portscan --set -j DROP
Sumber : https://8gwifi.org/docs/iptables.jsp
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar